Scripted REST API
INDEX
- What is Scripted Rest API?……………………………………………………………… 1
- Advantages of Scripted Rest API………………………………………………………. 2
- Roles Required……………………………………………………………………………. 2
- Fields of Scripted Rest API……………………………………………………………… 3
- Difference between Rest API and Scripted Rest API………………………………. 3
- Error Codes in Scripted REST API……………………………………………………… 4
- Example……………………………………………………………………………………. 4
1. What is Scripted Rest API?
Scripted REST APIs allow developers to create custom web service APIs in ServiceNow. These APIs enable external systems to interact with ServiceNow by defining endpoints, handling requests, and customizing responses beyond standard table APIs.
Using Scripted REST APIs, developers can:
- Define custom endpoints (resources)
- Configure HTTP methods such as GET, POST, PUT, DELETE
- Accept and process query parameters, path parameters, headers, and request bodies
- Write scripts to control request handling, business logic, and response formatting
Scripted REST APIs are created and managed using the Scripted REST Service form, available under:
Scripted Web Services → Scripted REST APIs
This is commonly used for:
- Integrating ServiceNow with external systems
- Exposing custom data and business logic
- Building reusable APIs for scoped applications
2. Advantages of Scripted Rest API
- It gives full control over how requests and responses work
- You can add custom business logic using scripts
- It can work with multiple tables at the same time
- You can return custom JSON responses
- It supports secure access using roles and authentication
- You can handle errors properly with clear messages
- It supports API versioning for future changes
- It is best for integrating ServiceNow with external systems
3. Roles Required
The role required to create and manage a Scripted REST API in ServiceNow is web_service_admin.
4. Fields of Scripted Rest API
Field Name | Description |
Name | Friendly name of the Scripted REST API |
API ID | Unique identifier used in the API URI |
Namespace | Application scope where the API is created |
Active | Enables or disables the API |
Default ACLs | Security rules applied to all resources |
Base Path | Base URL path for the API |
Version | API version for managing changes |
Short Description / Description | Explains the purpose of the API |
Security | Configure authentication and access control |
Content Negotiation | Define supported request and response formats (JSON, XML, etc.) |
Resources | Define API endpoints (URI paths) |
Request Headers | Define expected HTTP request headers |
Query Parameters | Define supported query parameters |
5. Difference between Rest API and Scripted Rest API
REST API | Scripted REST API |
Pre-built APIs provided by ServiceNow | Custom APIs created by developers |
Mainly used for standard CRUD operations | Used for custom logic and complex processing |
Limited customization | Fully customizable using server-side scripts |
Follows strict ServiceNow table structure | Can return custom response formats |
Faster to use for simple integrations | Best for complex and non-standard integrations |
Less control over request/response | Full control over headers, parameters, and payload |
Example: Table API, Attachment API | Custom endpoints under Scripted REST APIs |
No scripting required | Requires JavaScript scripting |
6. Error Codes in Scripted REST API
Error Code | Meaning | When It Occurs |
200 OK | Request successful | API executed successfully |
201 Created | Resource created | Record created via POST |
400 Bad Request | Invalid request | Missing/invalid parameters or payload |
401 Unauthorized | Authentication failed | Invalid or missing credentials |
403 Forbidden | Access denied | User lacks required role/ACL |
404 Not Found | Resource not found | Invalid endpoint or record |
405 Method Not Allowed | Invalid HTTP method | Method not supported for resource |
409 Conflict | Duplicate/conflict | Record already exists |
415 Unsupported Media Type | Invalid content type | Wrong Content-Type header |
500 Internal Server Error | Server error | Script error or exception |
503 Service Unavailable | Service down | API temporarily unavailable |
7. Example
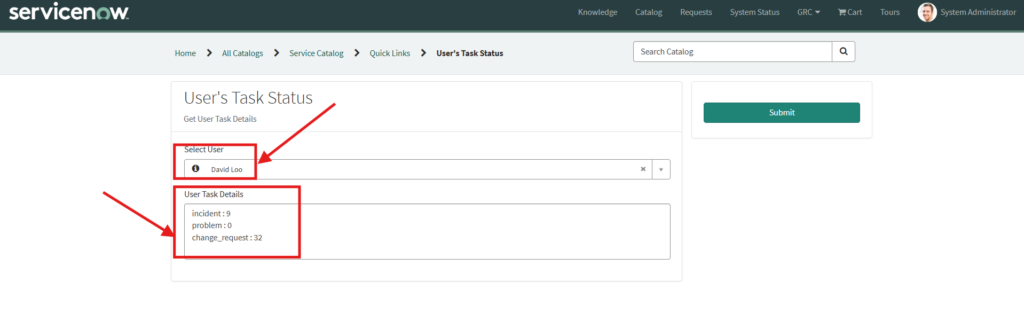
A catalog item named User Task Status exists in Instance A, which allows a manager to select a user to view the user’s task details. However, the actual task data (Incidents, Problems, and Change Requests) assigned to the selected user is maintained in Instance B. When the manager selects the User in catalog item in Instance A, the selected user information is sent to Instance B via integration. Instance B processes the request, fetches the count of Incidents, Problems, and Change Requests assigned to the user, and sends the response back to Instance A. The received response is then populated into the User Task Details variable of the catalog item.
Steps of Implementation:
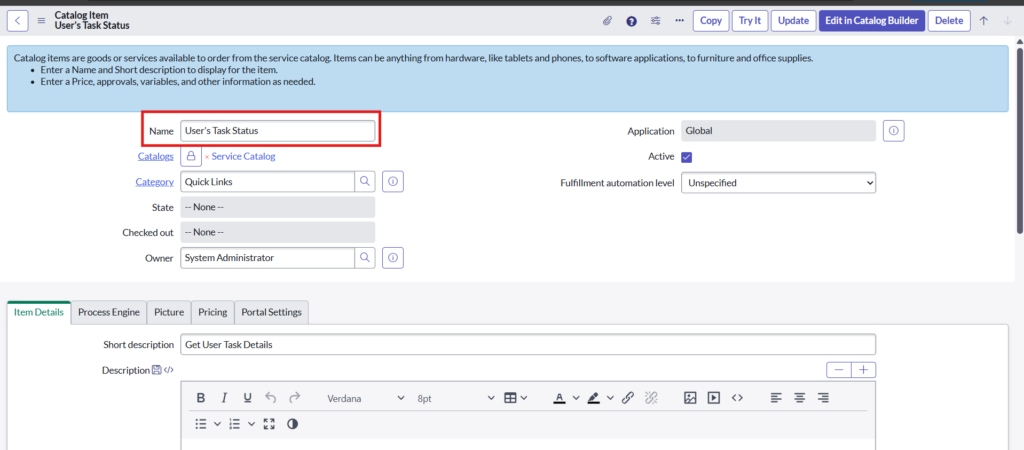
Step 1: Create a catalog item in instance A
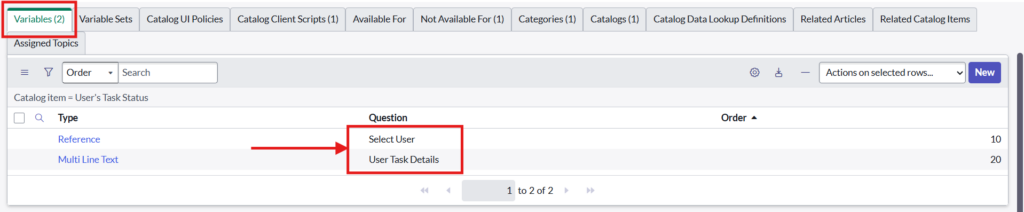
1.1. Create Variables
- Select User – reference – sys_user
- User Task Details – Multi Line Text
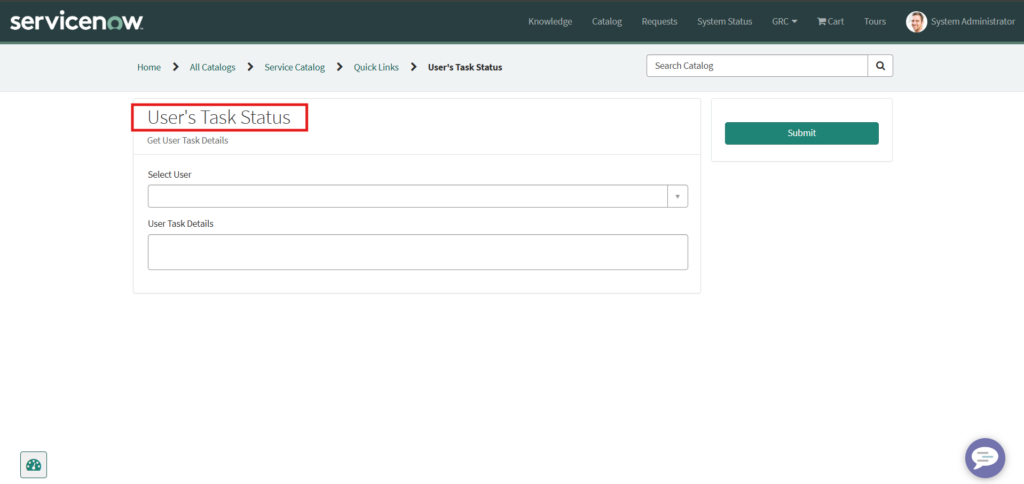
1.2. Final Catalog Item will Look Like this on Portal
Step 2: Create Scripted REST API in Instance B
Create a New Scripted REST API.
Navigate to ALL > System Web Services > Scripted REST API’s > New
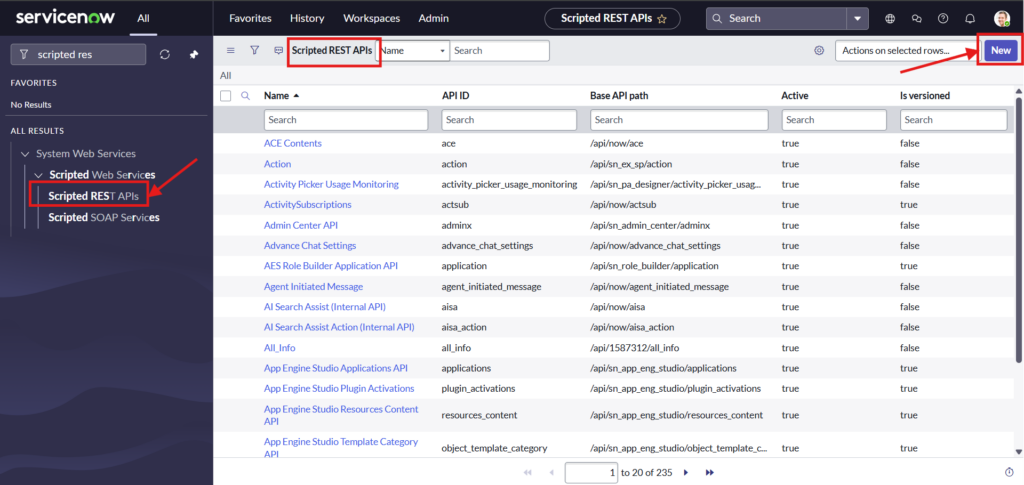
Give a name to new Scripted REST API and fill the mandatory fields as below:

2.1. Create Resource from related list
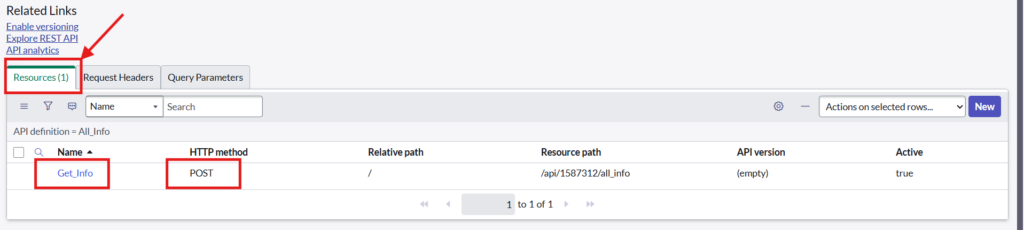
Give name to a New Resource and fill mandatory fields as below:
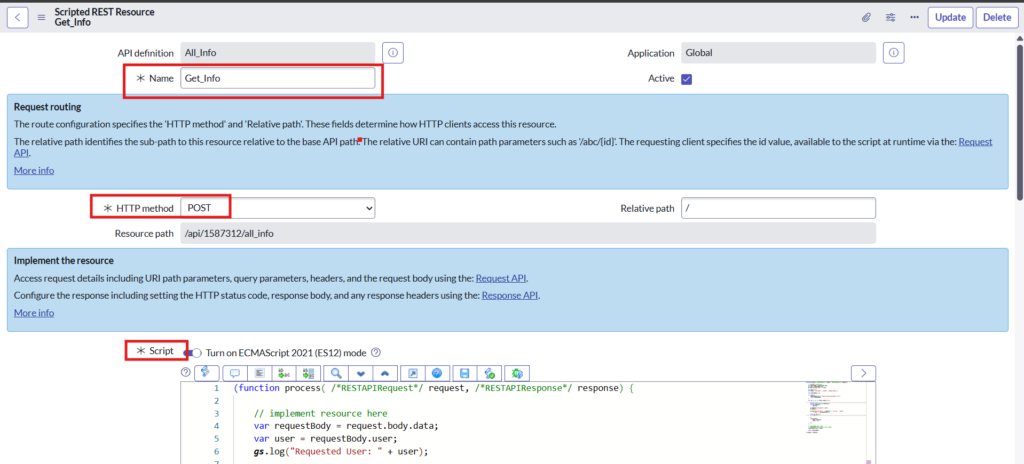
Script –
This script retrieves the user from the request body, fetches the assigned user details from the User table, and returns the data in the response body to Instance A.

Step 3: Create REST Message in Instance A
Navigate to ALL > System Web Services > Outbound > REST Message > New
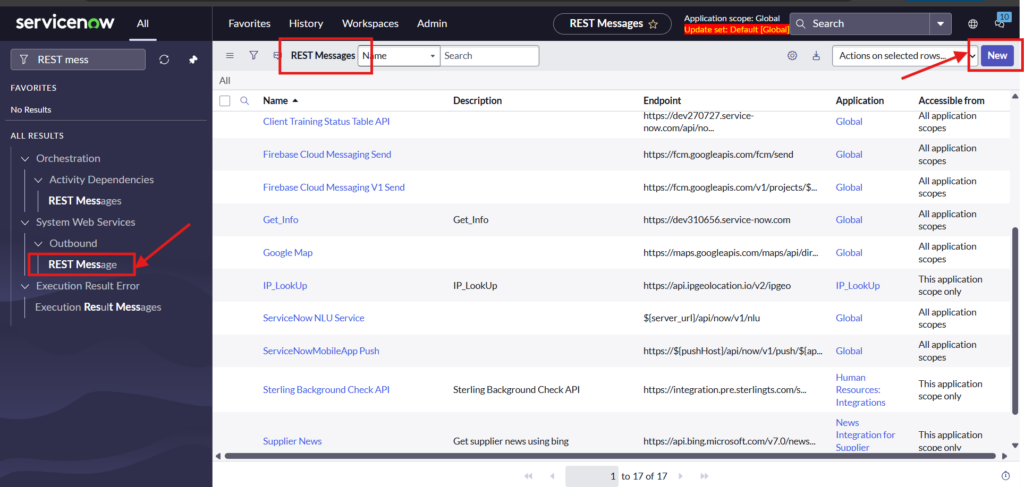
3.1. Provide Endpoint and Basic authentication details of Instance B.
Give name to REST message and Endpoint of instance B
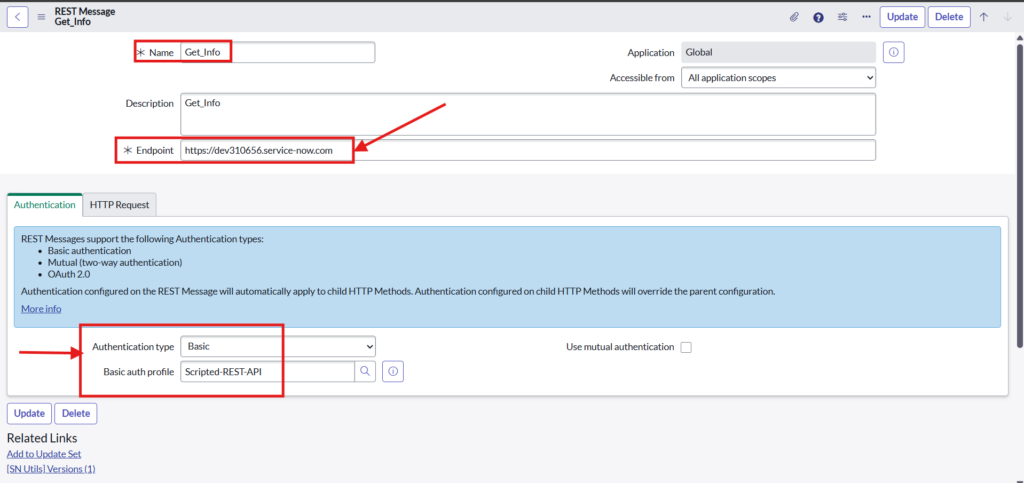
3.2. Basic Authentication Details
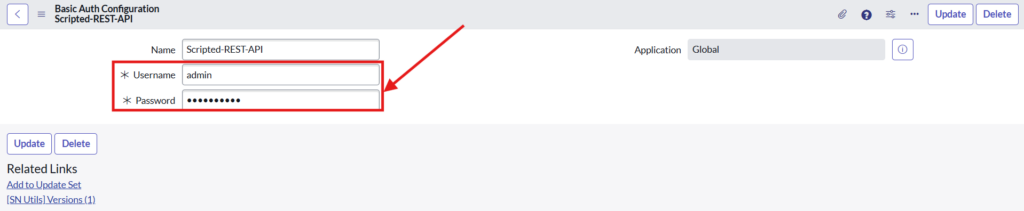
Fill username and password details of the instance B
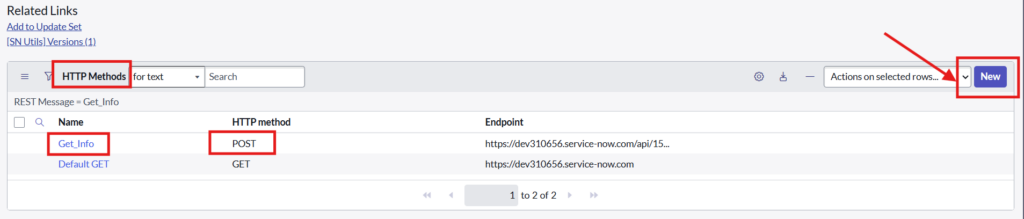
3.3. Create HTTP Method from related list
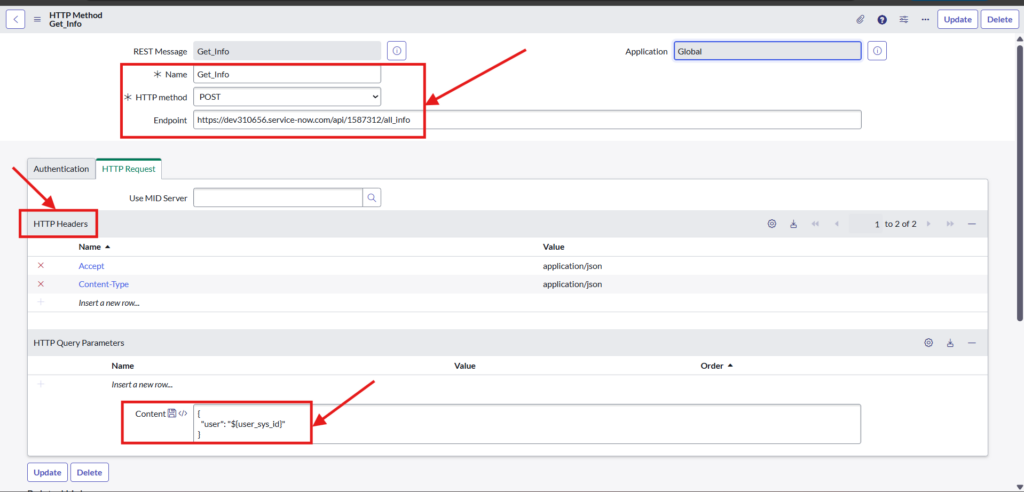
Select HTTP method, Endpoint, HTTP Headers and Query Parameters
Step 4: Create Script include to call REST Message in instance A
Navigate to ALL > System Definition > Script Include > New
Give a name to Script Include as below:
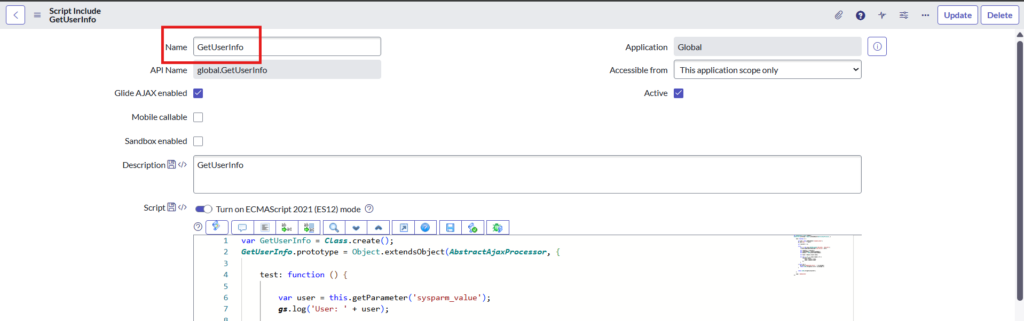
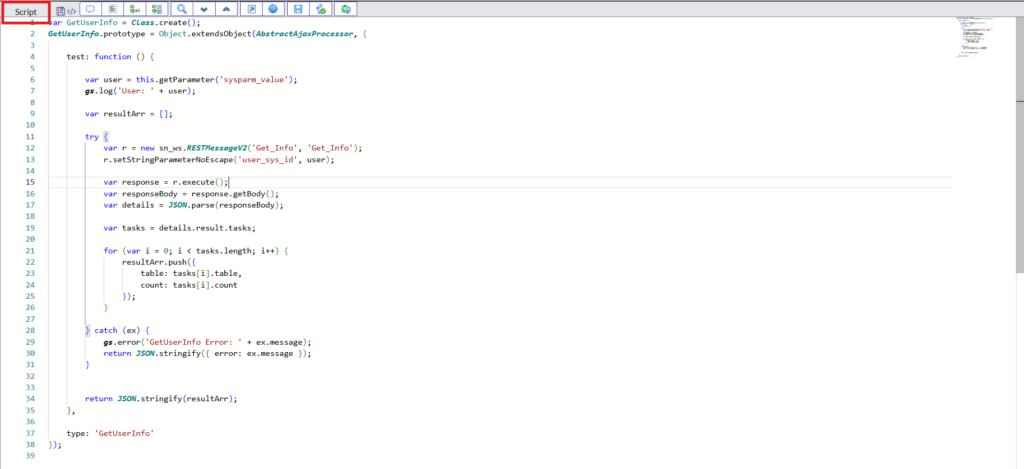
Script-
This script will fetch the user that is selected on the catalog item, calls the REST message we have created in instance A, and whatever response we get from instance B, script will fetch assignment details for the user.
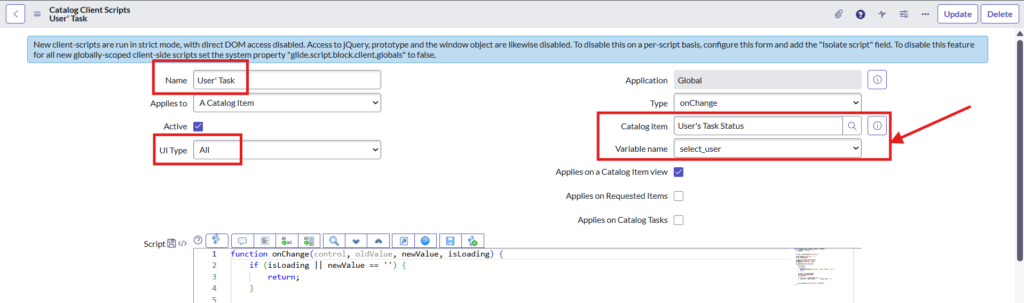
Step 5: Create catalog client script for your catalog item which is created in step 1
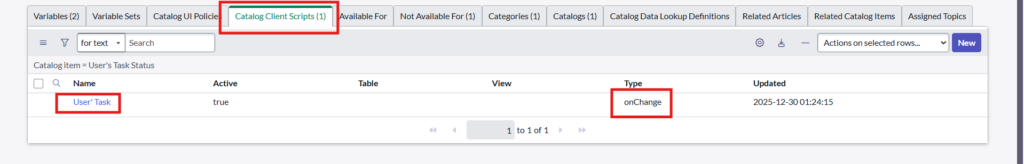
Fill the required details like Type, Catalog item, Variable Name and UI Type as below:
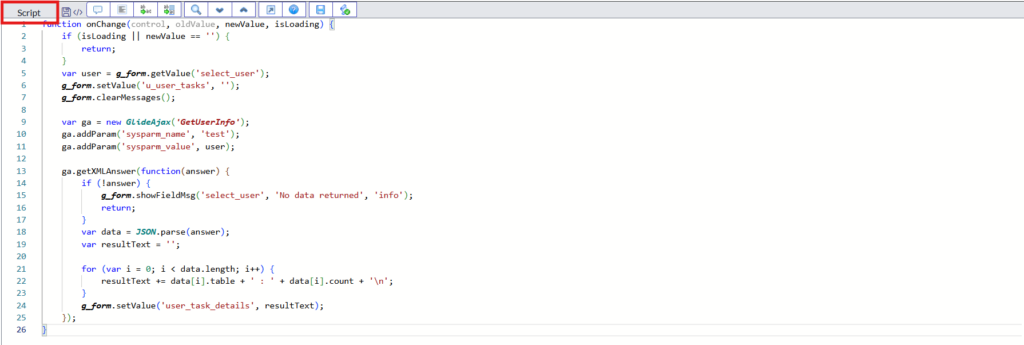
Script –
This script will get the value of the user from the catalog item. Also, once we select the user on catalog item, it will fetch the assignment details and that details will be populated in the ‘User Task Details’ field.
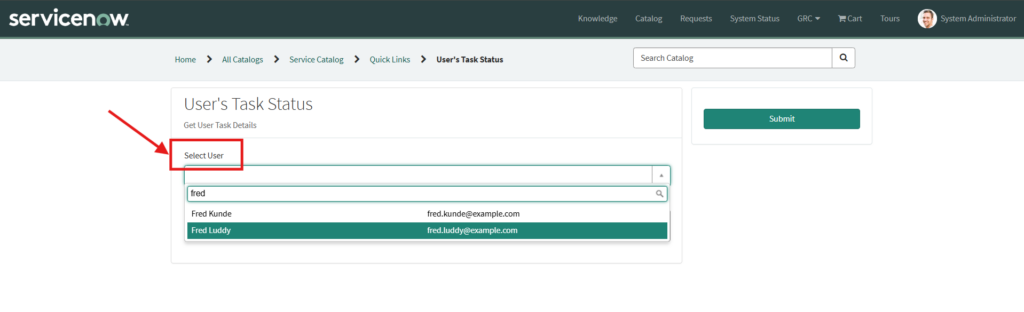
Step 6: Testing
Whenever manager selects a new user, whatever incidents, problems and change requests are assigned to that user count of that will be populated in the field.
You can see the details of the user has been populated in the User Task Details field.
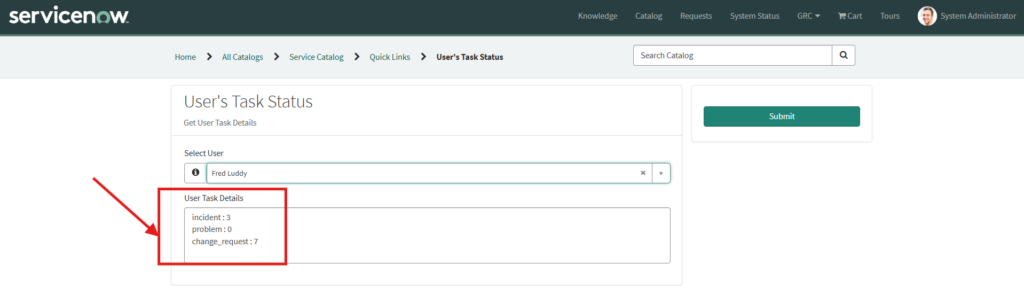
Similarly, if you select another user then his assigned tasks will be auto populated.